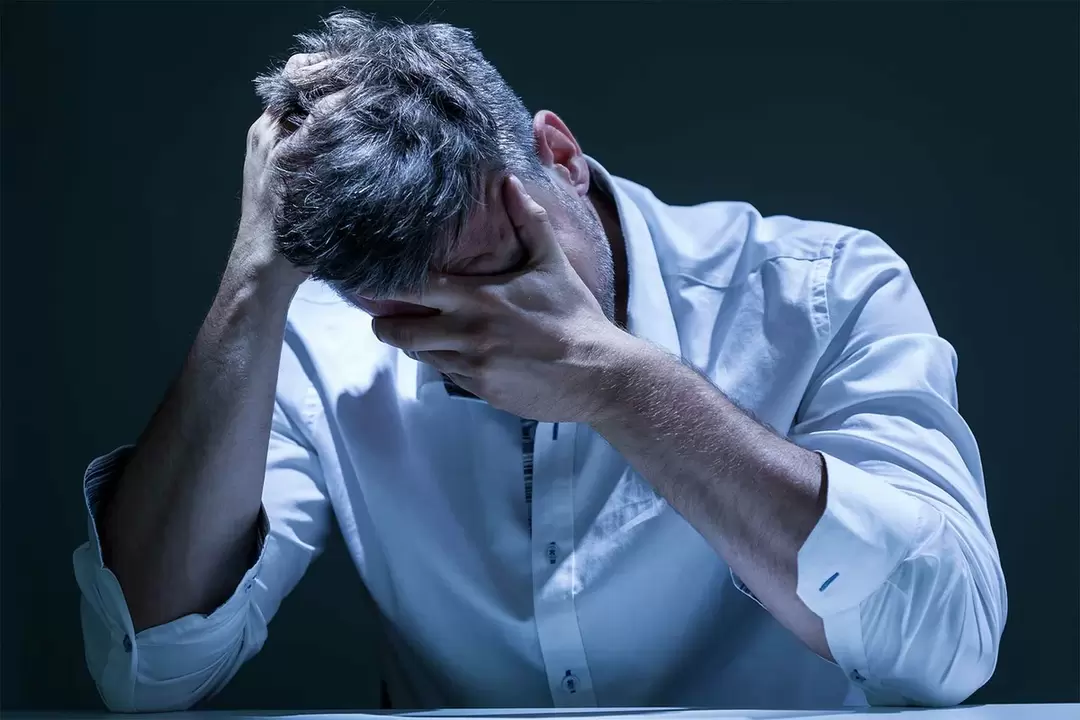
The term "prostatitis" refers to a chronic or acute inflammatory process of any etiology occurring in the prostate gland. Because the prostate is a purely male organ, prostatitis only develops in men. There are many types of prostatitis, but any prostatitis can be divided into acute and chronic.
Acute prostatitis occurs under the influence of many factors - the presence of bacteria, viruses, protozoa, diet, sedentary lifestyle, bad habits and others. >
The prostate is an external secretory gland, ie the secretion it produces enters the external environment. In humans, the prostate is an unpaired organ whose activity depends on male sex hormones, especially androgens and steroid hormones.
The prostate gland is located behind the bladder, squeezing the beginning of the urethra, where the ducts open.
Due to its location, the prostate is responsible for one of its functions - during an erection, it closes the outlet from the bladder. The prostate gland is responsible for the sensation of orgasm, which occurs due to the abundant supply of this gland with nerves, ie innervation.
Temperature
One of the first signs of acute prostatitis is a rise in temperature, regardless of the cause. As with any other inflammatory process in the body, the temperature rises to subfebrile levels - about 37, 5-380FROM.
Moreover, the more intense the immune response, that is, the higher the temperature. That is, at the peak of the disease, the body temperature can rise to forty degrees.
Of course, just a rise in temperature does not mean that prostatitis has occurred.
Usually, the first symptoms of prostatitis are difficulty urinating with the use of additional muscles - abdominal muscles, disruption of the mechanism of ejaculation, itching, burning and other unpleasant events in the perineum or genitals.
Frequent visits to the toilet
It is also an increase in urge to urinate (with a small amount of urine secretion), a feeling of "residual urine" after emptying the bladder, an unpleasant orgasm and a consequent decrease in libido.
General weakness
As with any other inflammatory disease, there is an intoxication syndrome accompanied by general weakness, decreased performance, nausea, and possibly vomiting.
There are also disorders of the nervous system - depression, nervousness and others.
What causes prostatitis
There are also risk factors for prostatitis - hormonal imbalances, including age, prolonged sexual abstinence, smoking, general hypothermia, fecal incontinence, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity, overheating, history of chronic sciatica, immunodeficiency, age-relatedchanges. body.
Particular attention should be paid to predisposing factors, such as inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, as the infection can spread upwards.
The disease begins with urethritis
The initial stage of prostatitis is characterized by a fairly typical clinical picture - lethargy of the urinary tract, the desire to urinate frequently, fever. Possible pain in the perineum. Often there is a violation of sexual function.
However, sexual dysfunction is more of a psychological aspect, physiological or clinical weeks. The process of ejaculation itself is either not pleasant at all, or even causes pain in which a conditioned reflex develops, which leads to a decrease in libido.
Purely physiologically, prostatitis can only lead to a lack of potential at a late stage. The initial stage is also called the "first symptoms" stage - the onset of urination does not occur immediately, as always, but with a slight delay.
The prostate is already enlarged at this stage, but it is still painless on palpation. At the same time, the borders of the prostate are well palpated and the median sulcus is palpated - as normal. The most interesting thing is that the phase of the first symptoms can last quite a long time - up to three years.
In recent years, the number of urologists is growing. That is, inflammation of the prostate gland "rejuvenates". This is due to the development of "unusual" recreation - surfing, diving, skiing and skiing. Prostatitis can occur with inadequate loads and complete hypothermia of the body.
And paradoxically, a very "quiet" lifestyle can also lead to the development of prostatitis. This is due to blood and lymph stasis in the pelvis - a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle is not the best way to distribute blood in the organs.
Inflammatory diseases that are not adequately treated and generally not related to the pelvic organs are also prone to prostatitis. This is due to the fact that the infection from the primary focus (of any etiology) can penetrate the prostate gland in a hematogenous or lymphogenic way. If there is a blockage in the pelvis, the infection settles there and begins to multiply.
This is because prostatitis is caused by stress. Stress weakens the immune system and thus increases the risk of prostatitis.
STDs - "sexually transmitted diseases" - are one of the main causes of inflammation of the prostate gland. Gonorrhea, when left untreated, almost always causes prostatitis.
But remember, you can't go from one extreme to another. With long-term sexual abstinence, blood and lymph stagnation reappears in the pelvic organs, a latent stagnation occurs in the prostate, which leads to prostatitis.
The prognosis is favorable for timely detection and adequate treatment of this disease, but if the disease is left to chance, it is possible to add a chronic or secondary infection, which will lead to very sad consequences.